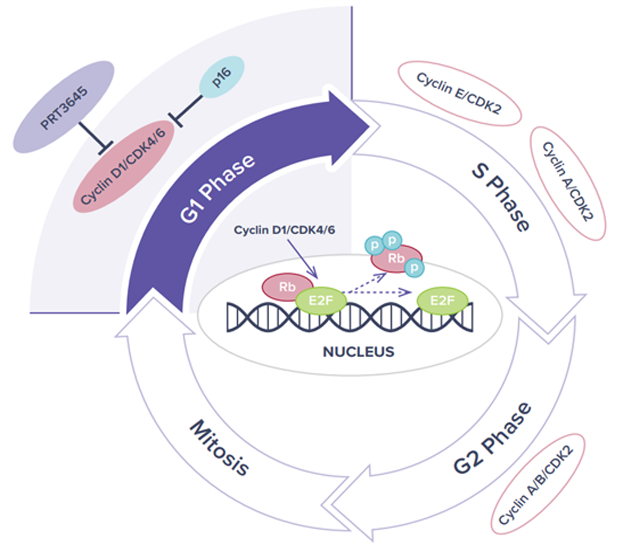
CDK4/6
Given the central roles that CDK4 and CDK6 play in cell cycle regulation, dysregulation of the CDK4/CDK6 pathway has been frequently observed in cancer and CDK4/CDK6 have been intensively investigated as potential therapeutic targets for cancer treatment. The approval of three CDK4/6 selective inhibitors in combination with endocrine therapies, to treat hormone receptor (HR) positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) negative metastatic breast cancer has further validated this hypothesis.
While FDA approved CDK4/6 inhibitors are highly effective for the treatment of ER+ metastatic breast cancer, the use of these drugs can also result in considerable levels of neutropenia and in some cases GI toxicities. Off target kinase activity and a higher degree of CDK6 inhibition may lead to these tolerability issues. A next generation CDK4/6 inhibitor with refined kinase selectivity has potential to be equally effective with an improved tolerability profile and extended utility, especially in combination therapies. In addition, current CDK4/6 inhibitors are limited by a lack of broad tissue penetration.
A next generation CDK4/6 inhibitor with improved tolerability and tissue penetrance could translate into activity in areas of unmet need beyond HR+ breast cancer.
Highly Selective, ATP Competitive
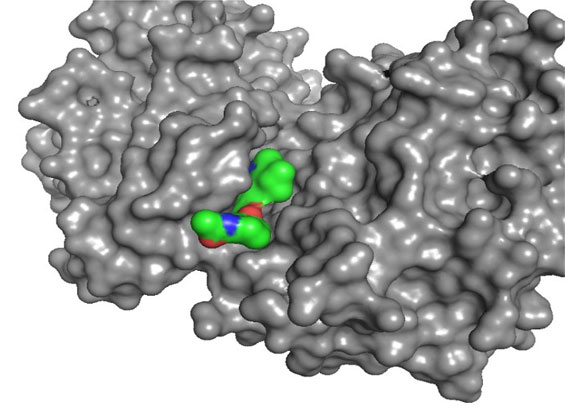
PRT3645
PRT3645 is Prelude’s next generation CDK4/6 inhibitor with high tissue distribution and brain penetration. In preclinical studies, PRT3645 treatment resulted in concentration-dependent inhibition of cell proliferation in both glioblastoma (GBM) cell lines and in ER+/HER2- and HER2+ breast cancer lines. In vivo, orally administered PRT3645 was well tolerated and highly efficacious in a dose-dependent manner in orthotopic human breast cancer brain metastasis and GBM models. Combined activity was observed when PRT3645 was dosed with inhibitors of the RAS pathway in NSCLC or CRC models or in combination with HER2 pathway inhibitors in HER2+ breast cancer models. This suggests a combination therapeutic potential in other tumor types with unmet need.
